Dear Mr. Electrician: What are the various electrical conduit types and their electrical code references? I would like to know the uses for each conduit type as described in the code book.
Answer: Below is a list of the common electrical conduit types installed in North America, with brief descriptions. The pertaining electrical code article numbers are listed in the descriptions.
NOTE: Text links below go to applicable products on Amazon, Redbubble, and eBay. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Using my links helps to keep this website FREE.
The many uses of conduit are not fully mentioned in this article, nor are all of the code requirements. Your best bet is to get a copy of the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) and read the relevant section for each particular electrical conduit type and other electrical requirements concerning your project.
Links to electrical conduit dimensions and hole saw sizes are listed at the bottom of this article.
All electrical conduit types are tested and approved for use with electrical wiring. Although it may appear the same, pipes used for plumbing or fences are not permitted for electrical work. It is important to match the electrical conduit types with the environment in which it will be installed to ensure a quality, long-lasting electrical installation.
Table of Contents:
- Conduit Fill
- EMT
- Rigid
- Intermediate
- Flexible Metal Conduit
- Liquidtight Metal
- PVC-40
- PVC-80
- ENT
- Liquidtight Non-Metallic
- Fiberglass
- HDPE
- Conduit Elbow Dimensions
- Conduit Dimensions
CLICK HERE to See Electrical Conduit Bending Books on Amazon
ELECTRICAL CONDUIT FILL
Below is a chart I found in an old book showing how to calculate conduit fill. Electrical conduits are limited to how much space the wire can use inside the conduit. The rest of the space inside the electrical conduit is for air so that the electrical wires can dissipate heat. Look up Conductor Fill in the back index of the National Electrical Code Book.
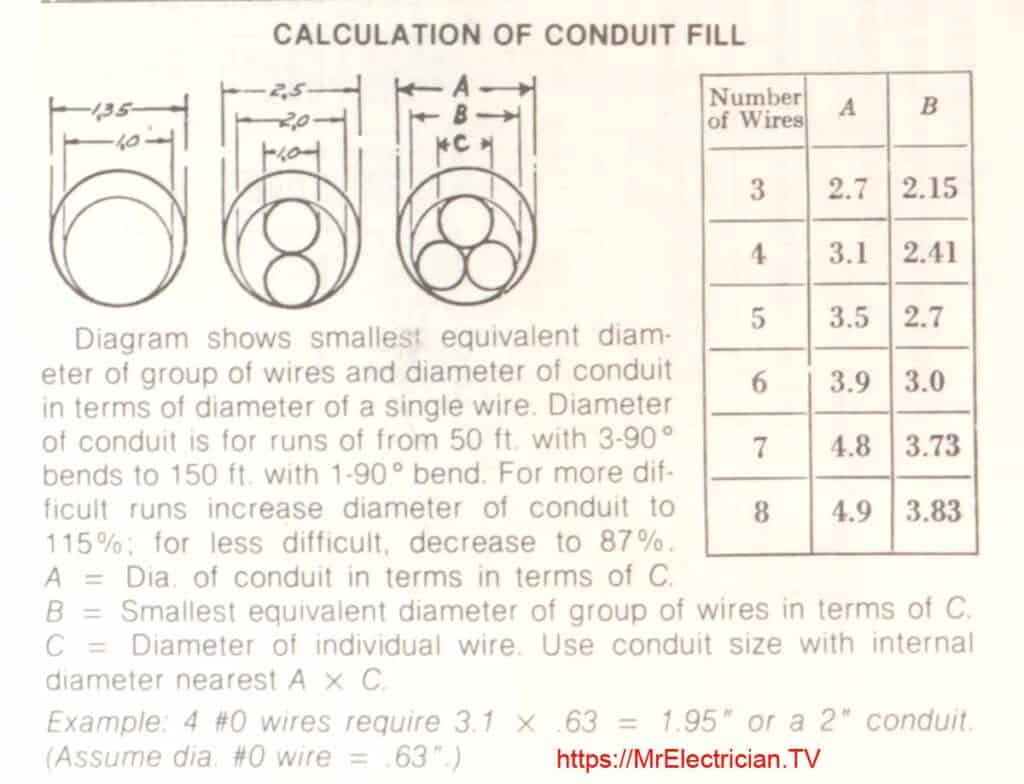
DESCRIPTION OF METAL CONDUITS
ELECTRICAL METALLIC TUBING (EMT or Thin Wall) is a smooth, lightweight, galvanized metal conduit that can be used in dry or damp locations. It is easy to work with and needs appropriate couplings and connectors when joined together or entering a junction box.
EMT can be bent using the proper bending tool for each designated trade size. The standard length for EMT is ten feet 10′ or 3.048 meters. Pre-bent elbows and twenty-foot 20′ (6.096 meters) lengths are available for some sizes. Tables C.1 and C.1(A) in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) tells you how many conductors are permitted in the EMT conduit.
Article 358 lists the installation requirements for EMT. It is manufactured in several colors to distinguish different electrical systems, such as fire alarm circuits from power circuits. EMT is mostly available in sizes 1/2″ to 4″ (16mm to 103mm).
RIGID METAL CONDUIT (RMC or Rigid or Heavy Wall) is a heavy-weight metal electrical conduit type with a galvanized finish throughout that can be used indoors, outdoors, and in the ground. It is factory-threaded at each end and is usually furnished with one coupling attached. Threaded and compression couplings and connectors are available. For hazardous locations, explosion-proof fittings are available.
The standard length for Rigid is ten feet 10′ or 3.048 meters. Pre-bent elbows and twenty-foot 20′ (6.096 meters) lengths are available for some sizes. RMC can be bent using the correct bending tool for each designated size. Tables C.9 and C.9(A) in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) tell you how many conductors are permitted in RMC conduit.
See Article 344 for Rigid Conduit electrical code installation requirements. It is available in 1/2″ to 6″ sizes or 16mm to 155mm.
INTERMEDIATE METAL CONDUIT (IMC) is a lighter-weight version of RMC. It has a galvanized finish inside and out and can be used in many of the same environments as RMC. It has factory threads at each end and is usually furnished with one coupling attached. It also utilizes the same threaded and compression couplings and connectors as RMC.
IMC can be bent using the proper bending tool for each designated size. The standard length for IMC is ten feet 10′ or 3.048 meters. Pre-bent elbows and twenty-foot 20′ (6.096 meters) lengths are available for some sizes. Tables C.4 and C.4(A) in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) tell you how many conductors are permitted in IMC conduit.
Article 342 details the requirements for installing IMC. It is available in sizes 1/2″ to 4″ or 16mm to 103mm.
FLEXIBLE METAL CONDUIT (FMC or Greenfield) is a galvanized finished flexible metal electrical conduit type composed of a continuously formed interlocking metal strip. It is for dry indoor installations. It is easy to work with and needs appropriate couplings when joining and connectors when entering a junction box. Bushings are usually required inside the conduit ends.
FMC is available in steel and aluminum. Dimensions may vary slightly between the two metal types. The same HW (Heavy wall) straps used for RMC and IMC can also support FMC. The minimum bending radius is 5 inches or 101.6mm, but increases for each size. The standard coil length is 100 feet or 30.48 meters. Also available on reels. Some electrical supply companies will cut it to length as needed. Tables C.3 and C.3(A) in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) show how many conductors are permitted in FMC conduit.
Article 348 has the code installation guidelines. Flexible Metal Conduit is available from size 3/8″ to size 4″ (12mm to 103mm).
LIQUIDTIGHT FLEXIBLE METAL CONDUIT (LFMC or Sealtight) is a flexible metal conduit with a non-metallic, non-conductive outer jacket that makes it suitable for use in wet locations. The minimum bending radius is 5 inches but increases for each size.
LFMC is terminated using metal connectors designed and approved specifically for use with it. It is available in 100-foot coils or on reels. Use the same metal straps as RMC. Many electrical supply companies will cut it to length. Tables C.8 and C.8(A) in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) tell you how many conductors are permitted in LFMC conduit.
Read about its approved uses in Article 350. Sealtight is available in sizes 3/8″ to 4″ or 12mm to 103mm.
NON-METALLIC CONDUITS DETAILS
RIGID POLYVINYL CHLORIDE CONDUIT (PVC) Schedule 40 is a nonmetallic, non-conductive electrical conduit that is good to use indoors and outdoors or underground. PVC conduit is sold with one coupling on one end. It has some flexibility, but it can also be heated and bent. Pre-bent elbows are available in some sizes.
Although there are PVC straps available, the same HW (Heavy wall) metal straps used for RMC and IMC can also support PVC. The PVC conduit is joined using special glue and the appropriate couplings and adaptors. PVC glue contains a solvent to soften the plastic, causing the pipe and fitting to weld together. When joining PVC, the glue must be applied to the conduit end and inside the fitting.
Do not use old cans of PVC glue, as most of the solvent will have evaporated, causing the glue to be less effective. PVC is available in lengths of 10 feet (3.048 meters) and 20 feet (6.096 meters). Tables C.11 and C.11(A) in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) tell you how many conductors are permitted in PVC schedule 40 conduits.
Read about PVC conduit’s expansion characteristics and how to compensate for them in Article 352. Schedule 40 is available in sizes 1/2″ to 6″ or 16mm to 155mm.
RIGID POLYVINYL CHLORIDE CONDUIT (PVC) Schedule 80 is a nonmetallic, non-conductive electrical conduit that is good to use indoors and outdoors or underground. Schedule 80 PVC has a thicker wall than Schedule 40. PVC conduit is sold with a coupling molded onto one end. It has limited flexibility but can be heated and bent to any angle. Pre-bent elbows are available in some sizes.
There are PVC straps available. However, the same HW (Heavy wall) metal straps used for RMC and IMC can also support PVC. PVC conduit is joined using appropriate fittings with special glue. PVC glue contains a solvent to soften the plastic, causing the pipe and fitting to be welded together. When joining PVC, the glue must be applied to the conduit end and inside the fitting.
Do not use old cans of PVC glue, as most of the solvent will have evaporated, rendering the glue less effective. PVC schedule 80 is available in 10-foot (3.048 meters) and 20-foot (6.096 meters) lengths. Tables C.10 and C.10(A) in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) show how many conductors are permitted in PVC schedule 80 conduits.
Read Article 352 about PVC expansion characteristics and how to compensate for them. Schedule 80 is available in sizes 1/2″ to 6″ or 16mm to 155mm.
ELECTRICAL NONMETALLIC TUBING (ENT or Smurf) is a nonmetallic, non-conductive flexible conduit. The minimum bend radius is 6 inches. Available in 10-foot (3.048 meters) lengths or coils and reels. There are couplings, fittings, and electrical boxes explicitly made for ENT.
Tables C.2 and C.2(A) in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) tell you how many conductors are permitted inside of ENT conduit.
Article 362 explains how ENT electrical conduit can be used. It is available in colors: yellow for communication circuits, red for fire alarms, and blue for power. Using the correct transition adapters is essential when terminating ENT into an electrical box. ENT is available in sizes 1/2″ to 2″ (16mm – 53mm).
LIQUIDTIGHT FLEXIBLE NONMETALLIC CONDUIT (LFNC or Carflex) is a nonmetallic conduit suitable for wet conditions. The minimum bending radius is 5 inches but increases for each size. LFNC is terminated using non-metallic connectors designed and approved specifically for its use. It is available in 100-foot coils or on reels.
Use the same metal straps as RMC. Many electrical supply companies will LFNC to length. Tables C.5, C.6, C.7, and C.5(A), C.6(A), and C.7(A) in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) tell you how many conductors are permitted in LFNC conduit.
See Article 356.2(1), (2), and (3) to understand the different types of LFNC. Carflex is available in 3/8″ to 2″ sizes (12mm – 53mm)
REINFORCED THERMOSETTING RESIN CONDUIT (RTRC or Fiberglass) is a nonmetallic electrical conduit type suitable for many conditions. Larger sizes are available in 20-foot lengths only. Pre-bent factory elbows are available. RTRC conduit can also be bent using heat and a hydraulic conduit bender. RTRC must be installed with fittings approved for this type of conduit.
Conduit and fittings are joined using a two-part epoxy glue. Conduit ends, and the inside of fittings must be sanded using emery cloth. Expansion couplings are required on installations over 50 feet long.
Article 355 in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) details the uses of RTRC conduit. See Chapter 9, Table 1 to determine the number of conductors permitted. Fiberglass is available in 3/4″ to 6″ sizes and 21mm to 155mm.
HIGH-DENSITY POLYETHYLENE (HDPE) is a non-metallic flexible conduit in long reel lengths to reduce joints and installation time. It is not used for exposed applications. Utility companies commonly use this conduit for underground use.
See Article 353 in the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) for its permitted uses. Read Chapter 9, Table 1, to determine the number of conductors allowed. HDPE is available in sizes 1/2″ to 12″.
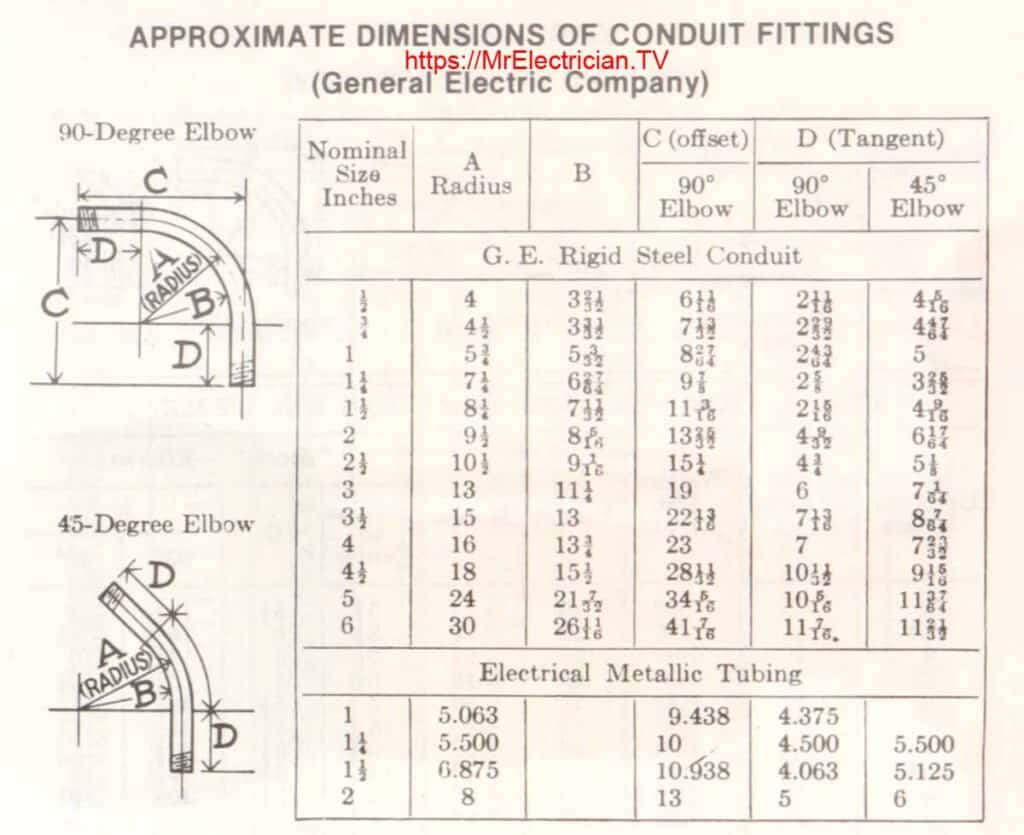
CONDUIT ELBOW DIMENSIONS
Below is a chart I found in an old book showing the approximate dimensions of factory-prefabricated rigid steel electrical conduit elbows and EMT elbows.
Other types of electrical conduit available, but not described here, are PVC Coated Metal Conduit, Aluminum Rigid, Stainless Steel, Innerduct, and Wiremold.
Most fittings for the various sizes and types of conduits, and even the conduits themselves, will not always be readily available. Distributors don’t like to keep things on their shelves too long; consequently, they stock items that sell quickly. Some more prominent electrical supply companies will have sizeable central warehouse hubs where stock is stored and delivered to their satellite locations. They should have inventories for many electrical conduit types.
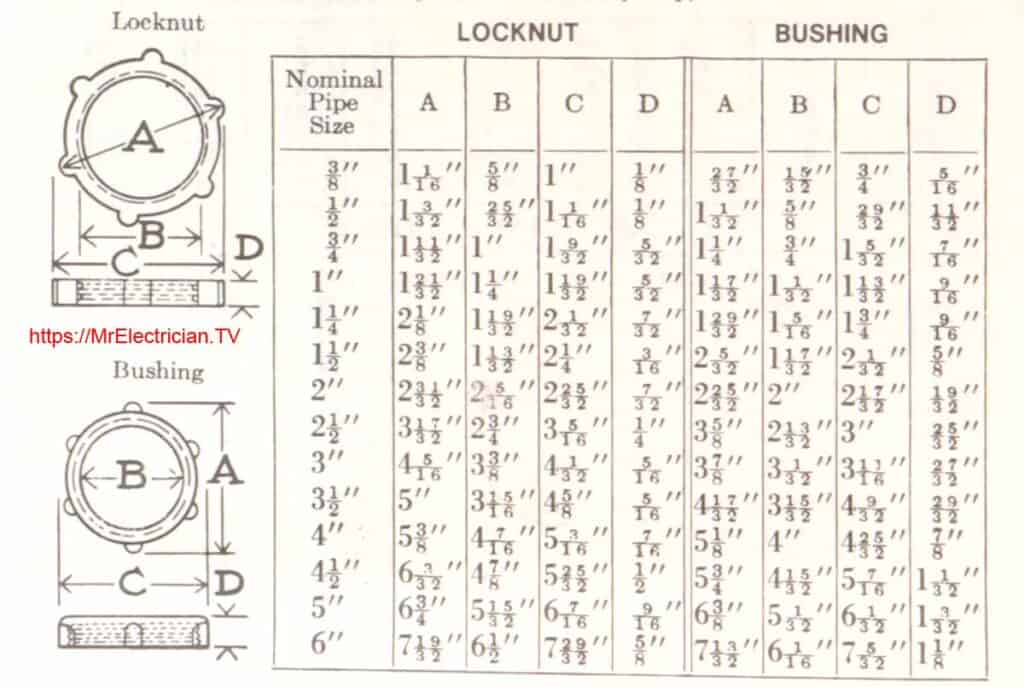
I found a chart in an old book depicting the dimensions of locknuts and bushings for all electrical conduit types.
Ten feet of conduit = 120″ (Inches), 3.333333333 Yards, 3048 Millimeters, 304.8 Centimeters, 30.48 Decimeters, and 3.048 Meters.
See my post on hole saw and knockout punch sizes to determine the hole needed for each size conduit.

Below is a chart I found in an old book depicting the weights and dimensions of electrical conduit types, including rigid conduit, iron pipe, and Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT). For more explicit conduit weight and dimension information, click on the individual conduit sizes underneath the chart.
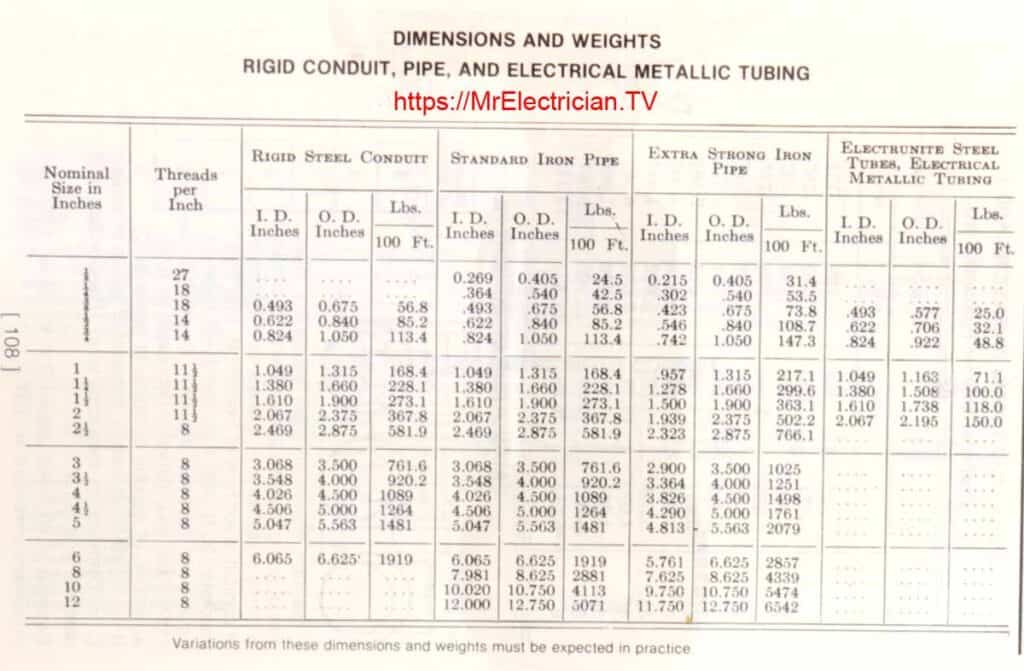
CONDUIT DIMENSIONS
Click the links below for the dimensions of each size electrical conduit type.

Click here to see the Specialized Electrician Tools I have used to simplify specific tasks.
Click here for an article about Electrical Conduit Types and Their Uses.
LINKS TO CONDUIT MANUFACTURERS
Aluminum and Steel Conduit Products – https://www.westerntube.com/
Fiberglass Conduit Products – https://championfiberglass.com/
PVC Conduit products – https://www.cantexinc.com/
Steel Conduit Products – https://www.alliedeg.us/
To help keep this website FREE, please use this Amazon link for your purchases. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Click for a FREE copy of my book “Almost Everything You Need To Know To Repair a Bathroom Exhaust Fan In Your Home.”
Get your required “Emergency Disconnect, Service Disconnect” labels and stickers to satisfy the 2023 National Electrical Code requirements in article 230.85(E)(1) and (2) by going to my Redbubble Shop here.
Visit my Link Tree home page for my social media connections and other links.










